electron affinity exceptions|how to tell electron affinity : Manila The electron affinity trend is explained in this video with all the exceptions you need to know, the definition of electron affinity, how to write the chemic. PinayFlex is a free Pinay porn site to watch Pinay scandal videos. Watch rare Filipina videos and other Asian amateur clips.
electron affinity exceptions,For example, the first electron affinity of oxygen is −141 kJ/mol, but the second electron affinity is +744 kJ/mol: \[O_{(g)} + e^- \rightarrow O^-_{(g)} \;\;\; EA_1=-141 \;kJ/mol \label{7.5.7} \]
Exceptions abound in electron affinity. Another case is in that of $\ce{F}$ versus that of $\ce{Cl}$. You would think that $\ce{F}$ being far more electronegative, . The energy change that occurs when a neutral atom gains an electron is called its electron affinity. When energy is released in a chemical reaction or process, .

The electron affinity trend is explained in this video with all the exceptions you need to know, the definition of electron affinity, how to write the chemic.The electron affinity (EA) is the energy change for adding an electron to a gaseous atom to form an anion (negative ion). This process can be either endothermic or exothermic, .
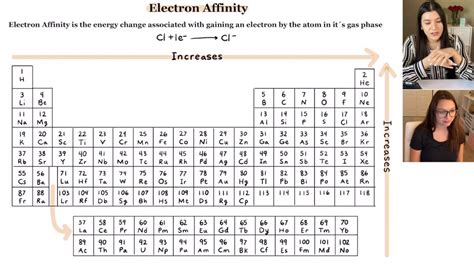
Unlike some of these other properties, there are many exceptions to the trends for electron affinity. Electron affinity general increases moving across a row or period of the periodic table , until you .
When an electron is added to a gaseous atom, a change in energy is observed called electron affinity. Electron affinity measures the ease of gaining an electron by an atom. . For electron affinity, going across a period on the periodic table, we see a little bit of a trend, but there are many exceptions to this, and perhaps our explanations are a little bit too .
Exceptions to electron affinity trends include the noble gases, fluorine and Groups 2, 14 and 15 in the periodic table. Learning Outcomes. After completing this lesson, students.electron affinity exceptions how to tell electron affinityChemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This process creates a negative ion. This process differs from .
Electron affinity is a measure of how readily a neutral atom gains an electron. Electron affinity ( Eea) is the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gas phase. In simple terms, it .

This chemistry tutorial describes the concept of electron affinity and covers the general periodic trend of electron affinity along with notable exceptions i. This chemistry tutorial describes the concept of electron affinity and covers the general periodic trend of electron affinity along with notable exceptions i.
Electron affinity is the energy change that results from adding an electron to a gaseous atom. For example, when a fluorine atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form F⁻ (g), the .
ExtensionOutrageous3. • 3 yr. ago. Electron affinity is the energy released when a neutral molecule or atom accepts an electron. But fluorine is the exception to this rule because fluorine is so small and highly electronegative that within its atomic radii electrons will be repulsing each other. To keep the electron in its orbital energy is .
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. For many atoms, electron affinity is exothermic. . Periodic Trends of Electron Affinity . There are many exceptions and deviations in the behavior of atoms toward adding an electron(s). However, let’s try to understand what properties of atoms .The electron affinity of an element is the energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. A fluorine atom in the gas phase, for example, gives off energy when it gains an electron to form a fluoride ion. F ( g) + e - F - ( g) Ho = -328.0 kJ/mol.
electron affinity exceptions The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (1.1.2.4.1) (1.1.2.4.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is . Electron affinity is defined as the quantitative measurement of the energy change that results from adding a new electron to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher an atom’s affinity for electrons.The energy of an atom is stated when an atom loses or gains energy . Definition of electron affinity Electron affinity is the affinity of an element to an electron. This is measured by the energy released when an element in its gaseous state accepts an electron to form an anion. . First electron affinity decreases down the group; Exceptions are nitrogen, fluorine, berylium etc. 4.81/5 (16) Please rate these .
The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (2.10.1) (2.10.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is required . However, there are few exceptions. The IE1 decreases when crossing from element in group 15 to the element in group 16. . Electron Affinities. Electron affinity, often abbreviated as EA, is the energy released when an electron is added to a valence shell of the atom. F(g) . When an electron is added to an atom, the energy change is .
The electron affinity (E ea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion.. X(g) + e − → X − (g) + energy. This differs by sign from the energy change of electron capture ionization. The electron affinity is positive when energy is released .
You must be thinking of the exception between the electron affinity of carbon compared to the electron affinity of nitrogen. Following the trend, one would expect carbon to have a lower electron affinity than nitrogen. However, because nitrogen has half-shell stability, it does not want to gain an electron. Carbon needs to gain 1 electron .
The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (2.8.1) (2.8.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is required .Figure 7.5.2: Electron Affinities (in kJ/mol) of the s -, p -, and d -Block Elements. The s blocks are purple, the p blocks are green, the d blocks are red, and the f blocks are blue. Electron affinity increases from left to right and bottom to top. Atoms with the largest radii, which have the lowest ionization energies (affinity for their own .
Definition of Electron Affinity. Electron affinity is a quantitative measurement of the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher the electron affinity and the more easily an electron is added to an atom. Electron affinity can be .
Electron affinity. The first electron affinity (EA 1) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms, to form 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a single negative charge under standard conditions; X(g) + e-→ X-(g). EA 1 is usually exothermic, as energy is released. Since this is generally an exothermic process, then .Electron Gain Enthalpy: Types, Electron Affinity & Exceptions. Electron gain enthalpy is defined as the amount of energy that is released or absorbed when a neutral isolated gaseous atom accepts an electron to form a negatively charged anion. This reaction can either be exothermic or endothermic, meaning, energy can either be released or .
electron affinity exceptions|how to tell electron affinity
PH0 · trend for electron affinity
PH1 · periodic trends exceptions
PH2 · how to tell electron affinity
PH3 · exceptions to orbital filling rules
PH4 · exceptions to electron affinity trend
PH5 · electron affinity vs electronegativity
PH6 · electron affinity values periodic table
PH7 · Iba pa